Introduction

Platform Components
The platform provides various components and tools that make it easier for solution developers to collect, model, store, manage, and query data in their solutions. This page will provide an overview of the platform’s components and their respective functions, as well as practical examples to illustrate their value and usage.
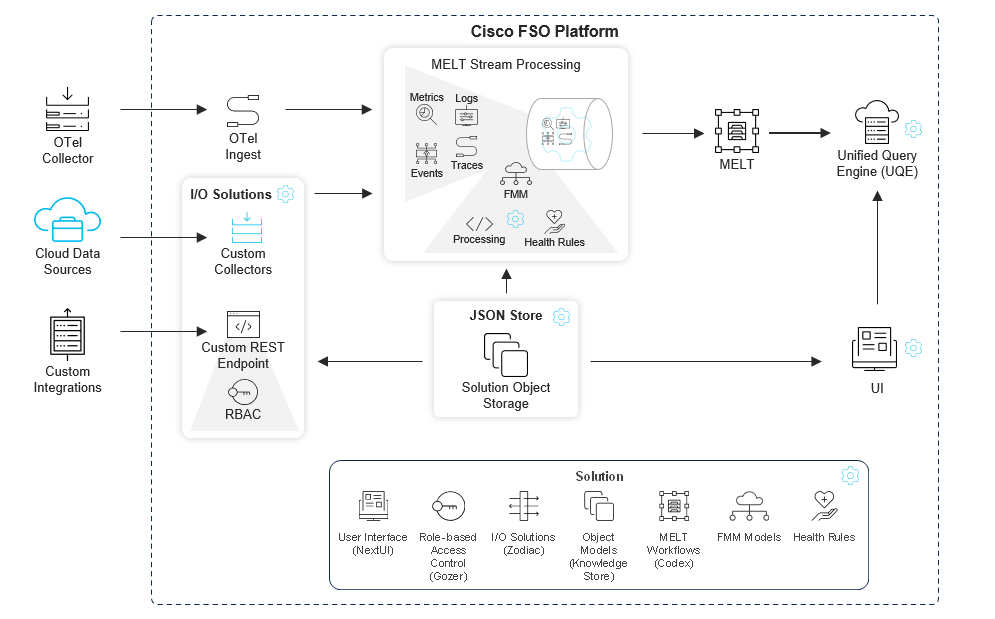
Read more about Platform Architecture Here
![]()
Knowledge Store - Storing Solution Artifacts
The Knowledge Store is an object and solution lifecycle management service and database for solution artifacts and user objects (such as dashboards and UI preferences). In addition, the Knowledge Store extends the platform into vertical applications requiring data other than metrics, events, logs, and traces (MELT).
Usage Examples
The solution developer will need to store data objects that can be created, read, updated, and deleted. The Knowledge Store provides this “CRUD” capability. The developer can also create and install “knowledge models” in the Knowledge Store to govern and validate data objects for solutions. Solution Services - Managing Services
Solution Services is an execution control plane for deploying and managing services. It allows solution developers to install, upgrade, and manage services without access to production clusters.
![]()
Access Management - Managing Access to Resources
Access Management controls access to APIs and resources for users and solutions. This extensible access control includes Attribute Based Access Control (ABAC) and Roles Based Access Control (RBAC). With RBAC, you can create new roles and permissions to protect endpoints to other components and entity models.
Usage Examples
Using Solution Services, your solution has added a REST endpoint for launching an investigation for root cause analysis (RCA), but you want to protect that endpoint with RBAC permissions. For example, you can define a new role named investigation:security_admin in Access Management and give this role the permission can_launch_investigation. This permission will be required for accessing the REST endpoint to launch investigations, thus, protecting sensitive knowledge from unauthorized access.
![]()
Extensible UI (DashUI) - Building UIs
DashUI is an extensible and configuration-driven platform for developers to build user interfaces (UIs) without writing source code. It is built on Next.js, an open-source web development framework for React, and uses React components as atomic building blocks.
Usage Examples
- Displaying headings, captions, labels, charts, and tables in a solution.
- Rendering one entity, a set of entities, or a group of entities.
- Creating templates as atomic building blocks for reuse in solutions.
![]()
Health Rules - Alerting
Health Rules allow solution developers to configure domain-specific rules and behaviors through configurations. It includes default health rules, health rollups, and entity-based health rules. Health rules can be simple, complex, and tied to alerts. Plaform health rules can be included with a solution, enabling a full-service experience for subscription applications and enrichments.
Cisco pioneered the use of health rules with entity modeling. While entities like “App” rolled up signals from thousands of observed nodes, the system still needed to “monitor itself”. Health rules do precisely that, and in the Platform, they can be customized along with your entity models. For example, you can monitor a Git repository by defining an entity model with Repo and Branch entities and then create health rules that will fire if tests are failing on the master branch. Usage Examples
- A Komodor solution can include specific health rules responsive to Komodor health logic—alerts generated by Komodor when health rules fire may consist of custom content.
- A Git solution that monitors Git repositories by defining entity models for repositories and branches and then sets health rules that fire if tests fail on the master branch.
![]()
Serverless Workflows - Executing Workflows
Serverless Workflows are capable of executing workflow that reacts to and transforms MELT data as it flows through the Platform. These Serverless Workflows can process a data stream before pushing it to the Knowledge Store. Developers create workflow definitions with custom logic for a particular service and store these workflows in the Knowledge Store, where multiple solutions can access and use them.
Usage Examples
- Redact PII in log messages.
- Generate metrics from logs.
- Generate ‘business metrics’ from spans.
- Look up geo names from IP addresses.
- Start a long-running ML job.
![]()
Unified Query Engine (UQE) - Querying Data
UQE enables solution developers to query data using the Unified Query Language (UQL), which is a Cisco domain-specific language used to observe data in the Cisco Observability Platform. Some of its features are:
- It is a domain-specific language for the MELT (metrics, events, logs, traces) model.
- It is a declarative language.
- It is a data query language.
- It is read-only.
- It presents MELT data and state in the scope of monitored topology.
All UQL queries are executed for a specific time range. UQL presents MELT data (metrics, events, logs, traces) and state in the scope of monitored topology.
Usage Examples
- MELT data: “Entities with more than 100 error log messages in last hour.”
- State data: “Entities with tag ‘region’ equal to ‘FRA’”
- Topology attributes: “Entities with type ‘Pod’” or “Interactions starting from Service 123.”
- Relationships: “All pods associated with Application 123.”
In the next section, Kickstart My Development you will learn what is needed to prepare your development environment on your local workstation.
After that, we’ll cover how to configure the FSOC Command Line Utility to access your platform tenant with the appropriate profiles.
![]()
Next Steps
Let’s get your development Kickstarted !!!